Alex Leeadded a note 17 days ago
After reading this, you will realize that the translation task is done. Future is the machine translation.
On March 18, 2025, NVIDIA made waves at the GPU Technology Conference (GTC) with the unveiling of its latest AI chips. The highlight of the event? The introduction of the Blackwell Ultra AI chips, promising groundbreaking advancements in computing power, memory capacity, and energy efficiency. But that’s not all—NVIDIA also laid out its long-term roadmap, teasing the Rubin and Rubin Ultra architectures set to redefine AI computing in the coming years.
The question now is: how will these innovations impact AI development, data centers, and enterprises relying on NVIDIA's hardware? Let’s dive into the key takeaways and discuss what this means for the future of AI.
Blackwell Ultra AI Chips: The Next Leap in AI Performance
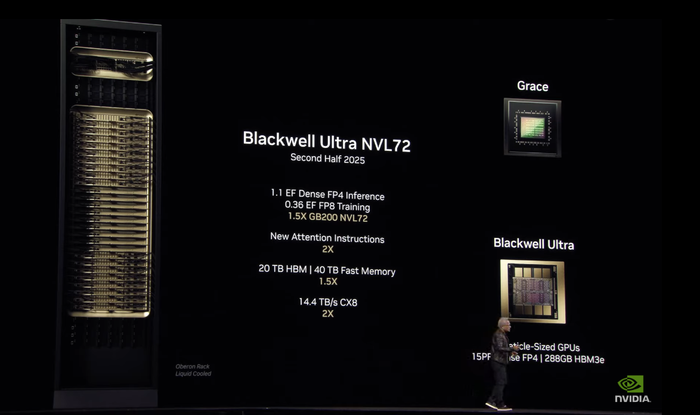
NVIDIA's Blackwell Ultra chips, set for release in the second half of 2025, are designed to push the boundaries of AI model training and inference. These GPUs aim to deliver unprecedented performance for large-scale deep learning applications. Here’s what makes them stand out:
Unparalleled compute efficiency for AI workloads
Expanded memory bandwidth to handle ever-growing datasets
Optimized power consumption, cutting operational costs for data centers
Enhanced multi-GPU communication, ensuring seamless scalability
These improvements signal a major shift in AI hardware capabilities, but how will this affect businesses, AI researchers, and cloud providers? Will this lead to even larger AI models, or will efficiency gains allow for more cost-effective deployments?
NVIDIA’s AI Chip Roadmap: What’s Next?
Beyond Blackwell Ultra, NVIDIA offered a sneak peek into the future with its Rubin and Rubin Ultra architectures:
Rubin Architecture – Expected launch: Second half of 2026
Rubin Ultra Architecture – Expected launch: Second half of 2027
With promises of even greater parallel computing power and energy efficiency, these chips could further revolutionize AI development. However, will they be enough to maintain NVIDIA’s dominance in a rapidly evolving AI hardware landscape?
The growing competition from AMD, Intel, and emerging AI chip startups raises an important discussion: Can NVIDIA stay ahead, or will alternative architectures gain traction?
The Broader Impact: AI, Data Centers, and Beyond
NVIDIA's new AI chips are poised to reshape multiple industries, including AI research, autonomous vehicles, robotics, and cloud computing. A major announcement that caught attention was the Dynamo Inference Service Software, designed to optimize inference workloads across large-scale GPU clusters.
With AI models getting bigger and demand for inference workloads increasing, the efficiency of AI infrastructure is becoming a hot topic. Could these new chips make AI inference more sustainable, or will energy consumption continue to skyrocket as AI adoption grows?
Moreover, how will cloud providers integrate these chips into their offerings? Will companies that sell GPU hardware, such as BuySellRam, see a surge in demand for used AI chips as businesses upgrade to Blackwell Ultra?
Conclusion: The Future of AI Computing
With the Blackwell Ultra AI chips launching soon and the Rubin roadmap on the horizon, NVIDIA is doubling down on AI innovation. But this raises several important questions:
Will these chips accelerate AI breakthroughs, or are we approaching hardware saturation?
How will enterprises and cloud providers balance performance gains with energy efficiency concerns?
Can startups and smaller companies keep up with the hardware demands of cutting-edge AI models?
The AI chip race is far from over, and NVIDIA’s latest announcements are sure to fuel discussions across